Thus for fast spreading centers the ridge stands at higher elevations than for slow spreading centers.
Sea floor spreading is driven by volcanic activity blank.
Convection currents carry heat from the lower mantle and core to the lithosphere.
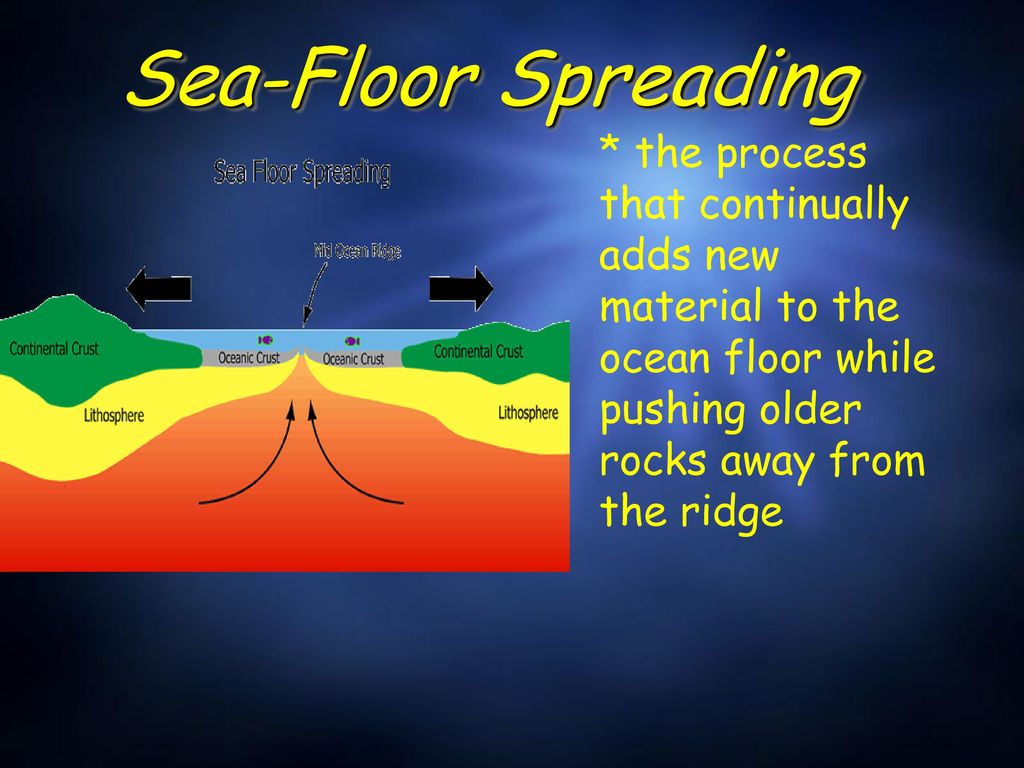
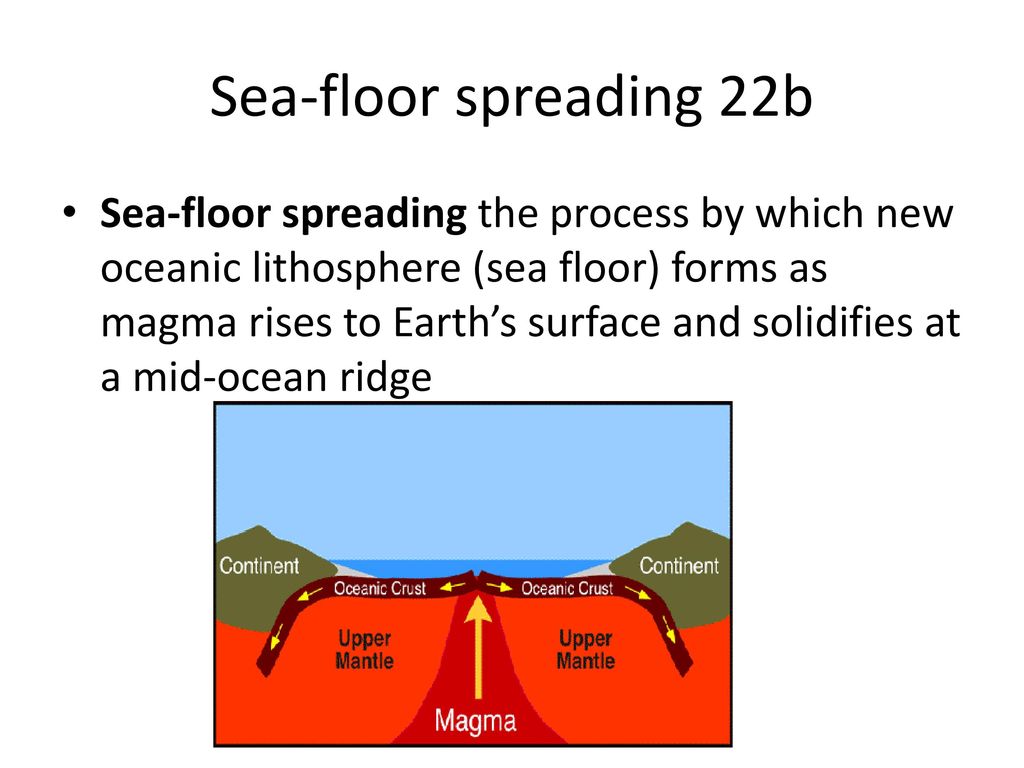
Seafloor spreading is a geologic process where there is a gradual addition of new oceanic crust in the ocean floor through a volcanic activity while moving the older rocks away from the mid oceanic ridge.
Sea floor topography is controlled by the age of the oceanic lithosphere and the rate of spreading.
Pangaea was one of several supercontinents that have formed and broken up during earth s history.
Spreading rate is the rate at which an ocean basin widens due to seafloor spreading.
Seafloor spreading at mid ocean ridges convection currents drive the movement of earth s rigid tectonic plates in the planet s fluid molten mantle.
Mantle convection is the slow churning motion of earth s mantle.
Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow.
Rates of seafloor spreading in the atlantic ocean are compatible with what is known about the breakup of pangaea.
Seafloor spreading is driven by volcanic activity that occurs.
Marine magnetic anomalies result from seafloor spreading in conjunction with.
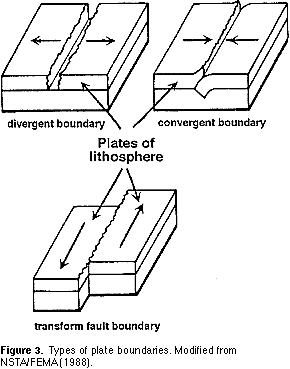
Seafloor spreading is the usual process at work at divergent plate boundaries leading to the creation of new ocean floor.
Rates of seafloor spreading in the atlantic ocean are compatible with what is known about the breakup of pangaea.
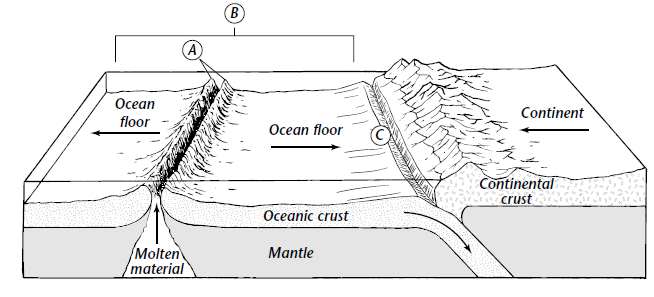
In places where convection currents rise up towards the crust s surface tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading fig.
Pipes pockmarks and localized amplitude anomalies mainly constitute the magmatic hydrothermal systems which are probably driven by post seafloor spreading volcanoes plutons.
As two tectonic plates slowly separate molten material rises up from within the mantle to fill the opening.
Seafloor spreading and other tectonic activity processes are the result of mantle convection.
Seafloor spreading is driven by volcanic activity that occurs.
The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate.
Hydrothermal structures such as pipes and pockmarks mainly occur in the proximity of volcanoes or accompany volcanic groups.