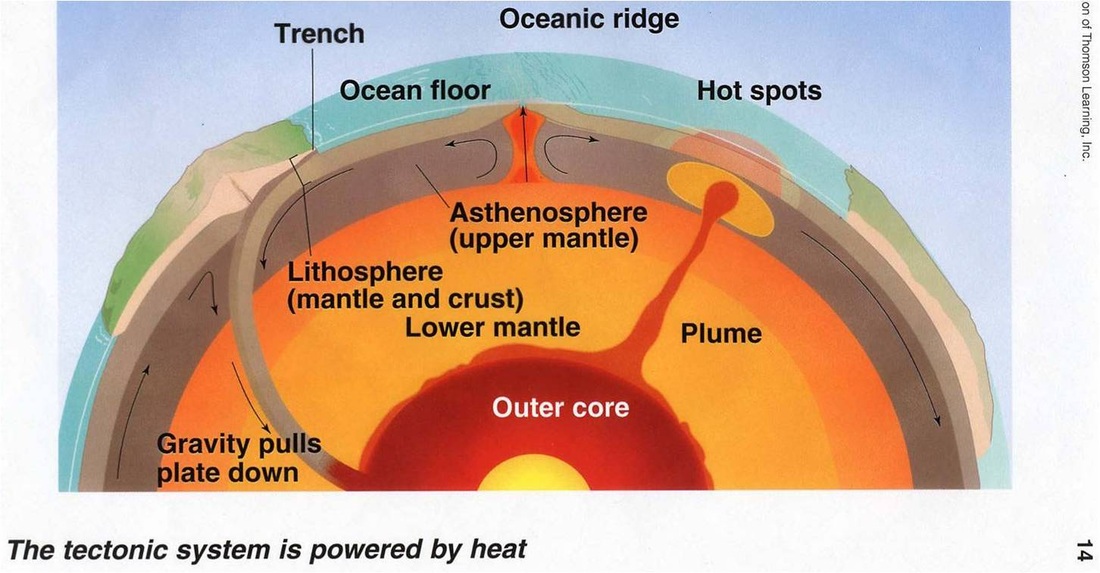
As tectonic plates slowly move away from each other heat from the mantle s convection currents makes the crust more plastic and less dense.
Seafloor spreading occurs at which type of plate boundary.
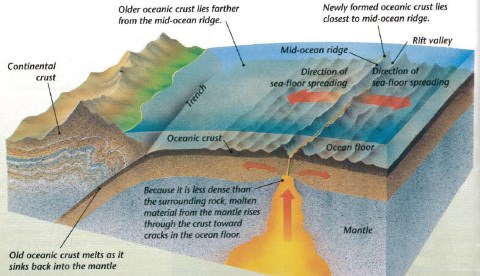
Seafloor spreading occurs at a diversion boundary.
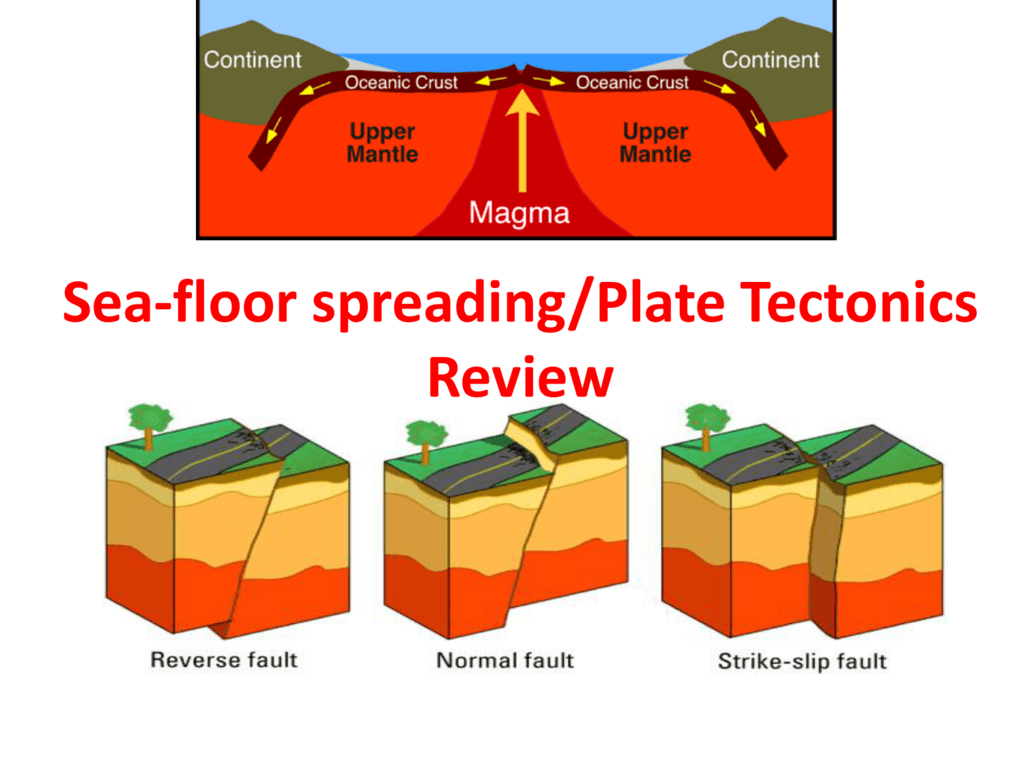
Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundaries divergent convergent and transform.
At this point tectonic plates pull away from each other and the gaps fills with magma from the mantle.
Along mid ocean ridges.
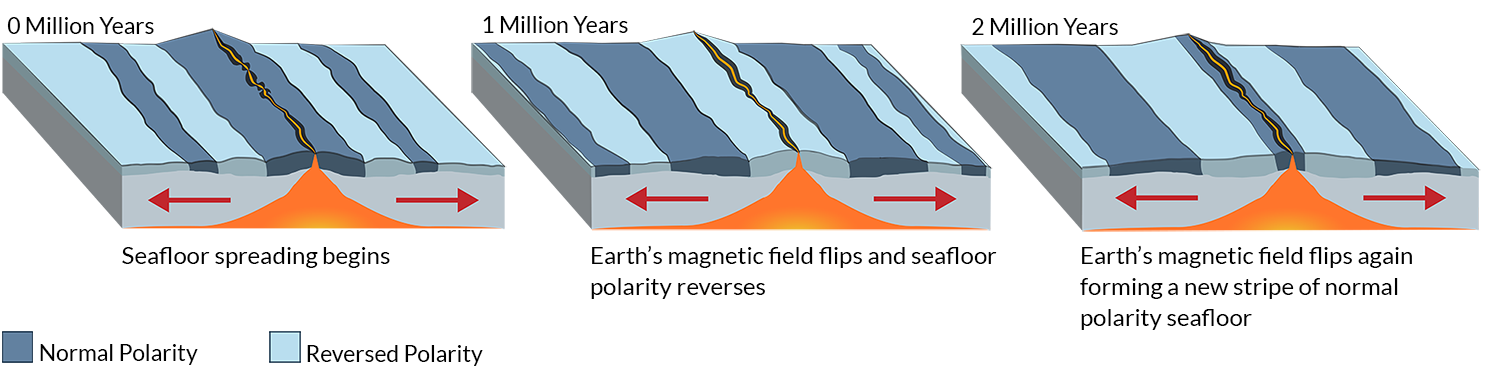
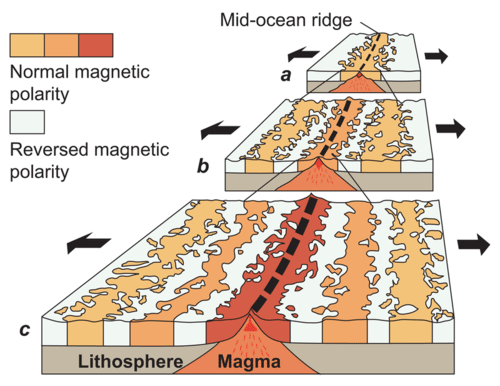
Convergent boundary because of the property of paleomagnetism.
What type of boundary occurs where two plates move together causing one plate to descend into the mantle beneath the other plate.
At divergent boundary there is a mid ocean ridge where the most recent material is still slightly lighter then the chilled product.
Seafloor spreading is driven by volcanic activity.
Rate of seafloor spreading.
Divergent or spreading adjacent plates pull apart such as at the mid atlantic ridge which separates the north and south american plates from the eurasian and african plates.
Seafloor spreading occurs at which type s of plate boundary.
A typical rate of seafloor spreading in the atlantic ocean is.
Scientists recognize three common types of boundaries between these moving plates.
Seafloor spreading occurs at boundaries.
At what plate boundary does seafloor spearing occur.
As the plates move past each other they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up.
Seafloor spreading occurs at divergent plate boundaries.
When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure energy is released as seismic waves causing the ground to shake.
Which basic type of plate boundary is shown in the image below.
At which type of plate boundary does seafloor spreading occur.
What did scientist use to prove the the seafloor was spreading apart.
Globally the rate of seafloor spreading takes place at the same rate as.
Lithosphere is destroyed at transform plate boundaries.
What type of plate boundary occurs where two plates are moving apart from one another.
The less dense material rises often forming a mountain or elevated area of the seafloor.